Sync Data from MySQL to MongoDB
Background
In many cases, we need to transfer MySQL data to MongoDB, such as:
- 「Database Switching」Transfer a database of MySQL instance to another MongoDB instance.
- 「Table Aggregation and Data Development」Merge multiple tables into one or split one table to many with UDF
The supported versions of MySQL and MongoDB.
Database Switching
Prerequisites
Source
| Filed | Value |
|---|---|
| Source Instance (MySQL) | 192.168.1.1 |
| Source Instance Port | 3306 |
| Source Database | Car_shop (already created) |
| Source Tables | All the table in Car_shop |
Target
| Filed | Value |
|---|---|
| Target Instance (MongoDB) | 192.168.1.2 |
| Target Instance Port | 27017 |
| Target Database | Car_shop |
Action
> # Create Source DataSource
> Source_Mysql = DataSource("mysql","Source_Mysql",'source').host("192.168.1.1").port(3306).username('root').password('password').db('Car_shop')
> Source_Mysql.save()
# Create Target DataSource
> Target_MongoDB = DataSource("mongodb","Target_MongoDB",'target').uri("mongodb://root:password@192.168.1.2:27017/Car_shop?authSource=admin")
> Target_MongoDB.save()
# Create a job that transform all the tables in Source-Mysql to Target-MongoDB.
> replication_job = Pipeline("replication_job").readFrom(Source(Source_Mysql,table_re=".*")).writeTo(Target_MongoDB)
> replication_job.start()
# Check the status of job
> show jobs
> monitor job replication_job
# Check the log of job
> logs job replication_job limit=5 tail=True
After these steps you can login to the target MongoDB and see the new data.
Table Aggregation and Data Development
Prerequisites
Source
| Filed | Value |
|---|---|
| Source Instance (MySQL) | 192.168.1.1 |
| Source Instance Port | 3306 |
| Source Database | Car_shop (already created) |
| Source Tables | Orders Products |
Target
| Filed | Value |
|---|---|
| Target Instance (MongoDB) | 192.168.1.2 |
| Target Instance Port | 27017 |
| Target Database | Car_shop |
| Target Table | Orders_and_Products |
Requirement
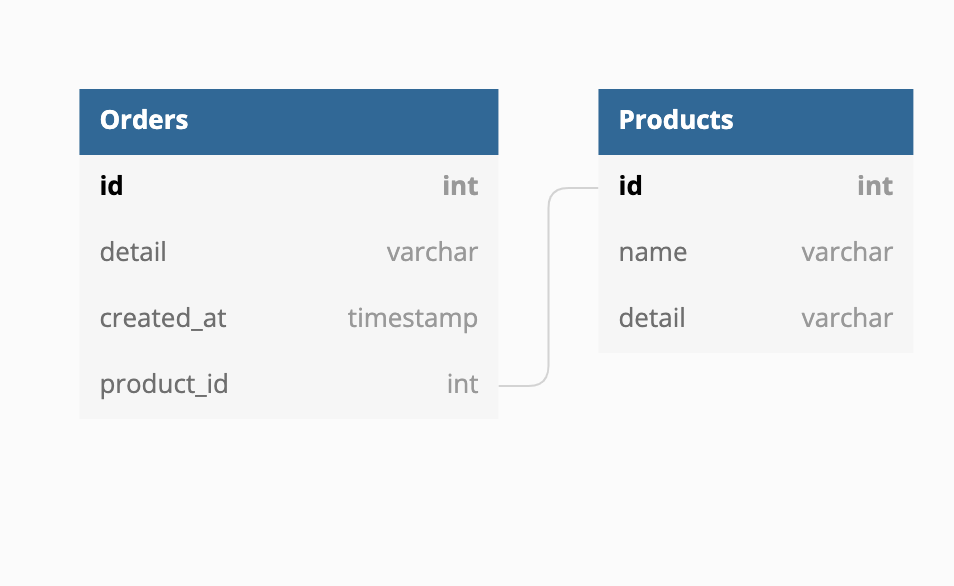

Action
# Write the js script 「find_product_name.js」
record["updated_at"] = new Date();
var rs = source.executeQuery({
sql: "select name from products where id = " + record.product_id + " limit 1"
});
if (rs) {
record["product_name"] = rs[0].name;
} else {
log.warn("Unable to find product_name is products tabel with : " + record.product_id);
record["product_name"] = "Not Found";
}
return record;
> # Create Source DataSource
> Source_Mysql = DataSource("mysql","Source_Mysql",'source').host("192.168.1.1").port(3306).username('root').password('password').db('Car_shop')
> Source_Mysql.save()
# Create Target DataSource
> Target_MongoDB = DataSource("mongodb","Target_MongoDB",'target').uri("mongodb://root:password@192.168.1.2:27017/Car_shop?authSource=admin")
> Target_MongoDB.save()
# Create a job that transform from Source_Mysql to Target_Mysql.
> replication_job = Pipeline("replication_job").readFrom(Source_Mysql.Orders).filterColumn(["id","detail","created_at","product_id"],FilterType.keep).js("/path/find_product_name.js").writeTo("Target_MongoDB.Orders_and_Products",writeMode=WriteMode.upsert, association=[("id", "id")])
> replication_job.start()
# Check the status of job
> show jobs
> monitor job replication_job
# Check the log of job
> logs job replication_job limit=5 tail=True
After these steps you can login to the target MongoDB and see the new data.